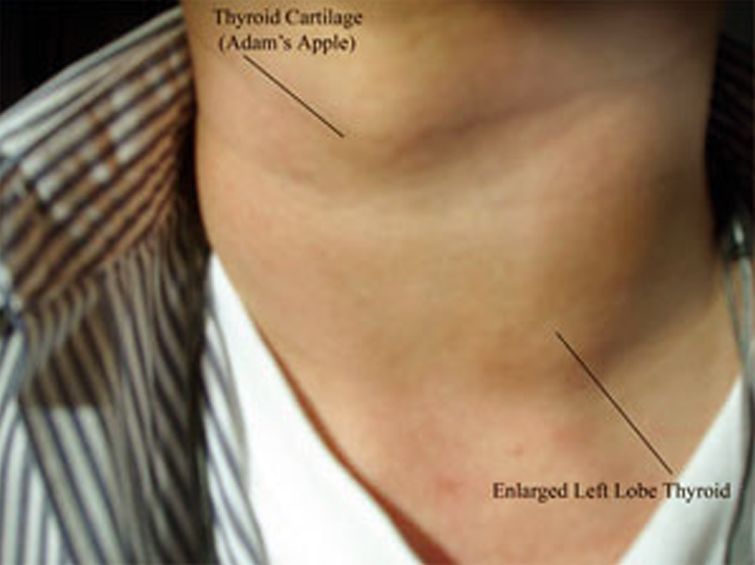
An enlarged thyroid is a common thyroid disorder. An enlarged thyroid is caused by an overactive thyroid hormone level. The thyroid gland is located behind the voice box and is responsible for making and secreting thyroid hormones that regulate growth and metabolism, as well as maintaining an even blood glucose level. The thyroid is also responsible for regulating the production of certain hormones that help to regulate the production of thyroid antibodies. When the thyroid produces too many hormones at one time, this can result in the gland oversecreting.
There are many causes for an overactive thyroid but in most cases the condition is caused by an underactive thyroid. In most cases, symptoms associated with an overactive thyroid include an increased heart rate, weight gain, depression, fatigue, loss of energy, swollen lymph nodes and weight loss.
Thyroid nodules occur when excess tissue is present in the thyroid glands. This extra tissue causes increased pressure on the thyroid gland as it is being produced. In some people, the symptoms will be more pronounced during periods of stress. An enlarged thyroid may also be due to an autoimmune response.
A goiter is another common thyroid condition. A goiter occurs when the lymph nodes become enlarged and create swelling and pain.
Symptoms associated with a goiter include pain around the neck, chest, back, or groin, fever, night sweats, and vomiting. Sometimes the goiter will spread to other areas of the body.
Another common type of thyroid condition is hyperthyroidism. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland has too much of a certain hormone (such as thyroxine). Symptoms of hyperthyroidism include weight gain, increased appetite, depression, palpitations, tremors, increased heart rate, constipation, sweating, and an irregular heart beat.
Another type of thyroid condition is referred to as sub-syndromal thyroid hypothyroidism. With sub-syndromal thyroid hypothyroidism, the thyroid does not produce enough of the hormone thyroxine to regulate the production of thyroid hormones.
To prevent the above conditions from occurring, treatment will depend on the cause of each condition. Some cases require a course of hormone replacement therapy while other thyroid conditions will only require that the thyroid is reduced in size.

In cases of hyperthyroidism, medications can be prescribed by your doctor to reduce or even eliminate the hyperthyroid condition. If your doctor determines that hypothyroidism is the cause, a course of hormone replacement therapy may be prescribed along with exercise and dietary changes.
Treatment of an enlarged thyroid is often done in conjunction with surgery. If surgery is required, it will usually occur only after the thyroid has been reduced in size to where it no longer has an excessive gland.
The surgery can be very small in scope, often removing just a small portion of the thyroid. or it may be larger and involve the entire gland.
If the surgery is for an enlarged thyroid, a follow up procedure may be required. This can either be radiation therapy or an iodine injection. In radiation therapy, radioactive iodine is injected into the gland to kill the cancer cells.
If iodine therapy is used, another follow up treatment is called cryosurgery. During this treatment, liquid iodine is injected into the area where the gland is located. It helps to thicken the blood to prevent infection and helps the body fight against infections.
Sometimes a surgical procedure is used to take out a large part of the thyroid. This is often a more aggressive type of treatment compared to the smaller types of surgical procedures used in combination with other treatment.
Medical research shows that patients of surgery and hormone replacement therapy are able to live longer and remain healthier than those who use more natural methods of treatment. The risk of surgery is generally less than using natural treatment, which can also help to prevent the symptoms of these conditions from developing into more serious conditions.
If you think that your thyroid is showing the symptoms of an enlarged thyroid, contact your physician for a medical treatment recommendation. You may be able to cure your enlarged thyroid right away with a proper diagnosis and the proper treatment.