Hepatitis C is a common liver disease, which is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV).
Hepatic is commonly transmitted through unprotected sex. Hepatic also causes serious complications in some people, but fortunately it rarely leads to death.
Hepatitis C, also known as Hepatitis B, is an easy-to-cure liver disease which is caused by HCV. When HCV enters the bloodstream, it multiplies and destroys the liver cells.
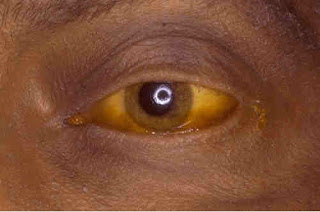
Hepatitis C can affect any organ of the body, though most frequently in the liver is affected. Most liver diseases occur around the age of 50 and this is the time when most patients begin to develop serious symptoms. Hepatitis symptoms include nausea, vomiting, jaundice, dark urine, muscle weakness, abdominal pain and abdominal tenderness, fever, loss of appetite, dark yellowish color to the skin or eyes, abdominal pain and weight loss, diarrhea, and bleeding in the stools.
Unfortunately, many people are unaware of the symptoms of hepatitis C. Although all people develop mild liver disease and other symptoms of hepatitis, the most common symptoms are jaundice and bleeding of the stool. The most severe symptoms are usually jaundice and liver failure.
If you are diagnosed with hepatitis C, treatment options are usually based on the severity of the liver disorder. Mild liver disease will respond well to antibiotics, while more severe cases may need liver transplantation.
The symptoms can be quite similar to those of other liver conditions so it’s important to get a diagnosis early in the course of the disease, or they may become fatal. Your doctor can often take tests to help diagnose the condition and determine the cause.
Treatment options depend on your condition, so it is best to discuss what options are available with your doctor. You may be prescribed anti- HCV medication, or even anti-rejection medication if you already have a liver transplant.
If you are suffering from liver failure or have had a previous liver transplant, you should avoid sexual intercourse until your doctor advises you otherwise. You should also avoid any contact with the patient’s blood.