Autoimmune diseases, also known as autoimmunity, affect nearly half of all people.
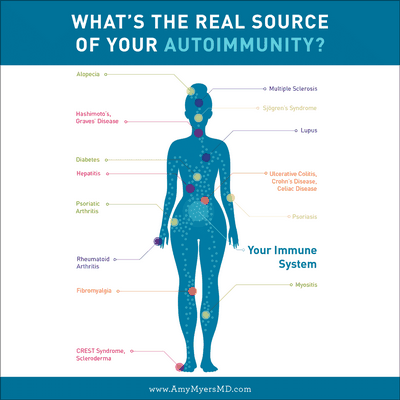
In fact, an estimated 40 million people suffer from autoimmune disease at any given time. These conditions may be hereditary or they can be caused by medications, foods and environmental factors. In women, the most common autoimmune diseases are: rheumatoid arthritis and Lupus. Lupus is the third most prevalent autoimmune disease in females.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an inflammatory disease that attacks the large joints in your body. It’s characterized by inflammation of the joints and usually results in stiffness, pain and redness. The most common autoimmune disease in women is: Lupus. Lupus is an autoimmune disease in which patients have antibodies that attack their own cells, resulting in severe inflammation and damage to the tissues around the joints and surrounding organs.
Autoimmunity is the medical term for an immune system response which occurs against something as simple as a virus or bacteria.

The immune system has an innate capability to fight off these types of invasions. When it isn’t properly controlled, however, it can become overactive and the result is a reaction against healthy tissue. The immune system responds to the invaders in a variety of ways. When the body becomes overly sensitive to substances, the body begins to attack the immune system itself and can lead to chronic health conditions.
Autoimmune diseases are a collection of symptoms caused by autoimmune reactions that can occur in a variety of areas of the body. Some of the more common areas affected are the kidneys, lungs, brain, liver, heart, bones, heart valves, intestines, lungs, skin, blood and joint cartilage. While some autoimmune conditions only affect a specific area of the body, other autoimmune disorders can affect any part of the body at anytime.
In Lupus, the body produces antibodies that attack the protective, fluid-producing blood cells of the body, resulting in the development of ulcers, rashes, and even gangrene. This condition results in pain, bleeding, mobility problems and sometimes, organ failure. Autoimmune diseases can also cause kidney failure in the elderly and may affect the liver and heart valves of the kidneys.
They can occur at any age and in men and women. An increased likelihood of developing autoimmunity has been associated with a decreased ability to resist certain types of cancer, so it’s important to monitor your health and to be tested for certain diseases.
In women, menopause is the main trigger for the onset of autoimmune diseases. During this time, hormone levels in the body begin to fluctuate and when they start to rise, the body begins to respond by producing more antibodies against healthy tissue. Menopause can also trigger the production of antibodies, which attack healthy cells in the liver and kidneys.
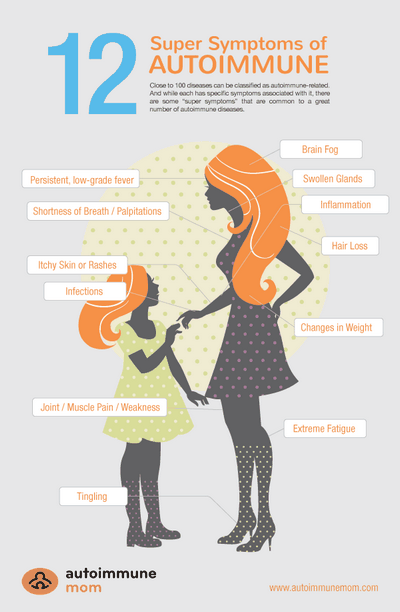
Many times, people suffering from autoimmune disease are unaware of the fact that the condition exists and that they may be infected with certain diseases themselves. Because the symptoms can mimic those of other diseases, it’s easy to miss potential illnesses and not seek medical attention until symptoms become too serious to ignore. It’s important to know the signs of a health condition and to get your doctor to test you regularly for specific diseases.
Because the cause of autoimmune disease is often unknown, treatment for autoimmune disease can vary greatly. For example, there may be no noticeable symptoms at all, and therefore doctors may choose to try a different approach to the problem than they would if the cause of the autoimmune disease were known. The goal is to prevent the disorder from spreading throughout the body, allowing the person to live a healthy life.